It has never been easier to build a great new website. And yet, getting that site to rise up to the top of the search results is a whole different story. Without the best search engine optimisation (SEO) tips and tricks, your website may end up left in the dark — without visitors, clicks, or sales. The good news is: SEO really isn’t rocket science. There’s no need to spend hours agonising about how to bring in traffic. Mastering SEO takes just a little time and effort. This can be made especially easy with the right tools (and there are plenty of them out there). In this guide, we will go over the main pointers to help you get to grips with SEO. You’ll also find a downloadable checklist at the end of this article, so that you can tick off best SEO practices as you go along.
What are search engines looking for?
Search engines like Google and Bing want to direct users to websites and content that is relevant to what they’re searching for. How exactly do they go about it?
There are four main elements that search engines look towards to work out where results should rank on their Search Engine Results Page (SERP). This depends on the algorithms (and Google keeps the exact recipe a secret), but the key factors are:
- Content: Is the content relevant to what the user is searching for?
- Performance: Does the site load fast and does it work properly?
- Authority: Is the content useful enough to link to or do other authoritative sites use that website as a reference or cite the information that’s available?
- User experience: How does the site look and behave? Is it easy to navigate around? Does it look safe? Does it have a high bounce rate?
With a view of the most important elements you need to focus on when optimising your site, here are the vital search engine optimisation hints to get your site ranking higher:
Step 1: Choose a great domain name
A good domain name is like your HQ online, representing your brand and making it easier for users to find and remember your site. You’ll want to choose the best possible domain name for your site. Doing so can impact your search visibility, your credibility, and the overall user experience. When selecting this important piece of digital real estate, think about:
Branding potential. It’s easier to build credibility and links to branded domains as people will take a yourcompany.uk more seriously than keyword-keyword.uk that isn’t fooling anyone. A branded domain can help build trust online and also increase the value of your content. When searching for your domain, use a domain search tool like the one we have at 123 Reg that allows you to check if your desired name is available. Be sure to check out our post on choosing a business name and a domain name to get a sense of what to focus on when choosing a good one.
Similarity. You’ll generally want to avoid being confused with other, more established brands. If your domain’s too similar to something else, you’re difficult to find.
Social Media Potential. Once you know that a domain name is available, check if the big social media handles still are, too.
Spelling matters! If your name is hard to spell, that means it’s easy to miss. People find you both online and by word of mouth. Keep it short, simple, and stickable!
What if you decide to buy an old domain instead of a new one? That can work, but if you’re buying a domain that has been owned by someone else, make sure the previous owner hasn’t done anything shady that might negatively affect its SERP ranking. Find out more about buying pre-owned domains and how to make sure there aren’t any issues you might inherit.
Step 2: Research for the right keywords
Keywords are like magnets to a search engine — attracting users to your webpage by matching what they’re looking for, and boosting your SERP visibility as they do so. It is important to do some keyword research to find out the words your audience are searching for in relation to your products or services.
Before you get started with your keyword research, ask yourself:
- What is your page about? Is it about a product or service you’re selling, like water heaters or burst pipe repair? Or a useful how-to guide on how to fix a garbage disposal unit. When you know what will be the main topic and what information you’ll include, you’ll have an easier time determining the type of keywords you’ll need to target on that page.
- What is the main intent of the page? What are your main goals for this page? Is it to sell a product or a service, or is it to provide more information that can help visitors make an educated decision? By figuring out the main intent for a page you’ll be able to focus on more relevant keywords, rather than generic ones.
Search engines like Google consider both ‘short-tail’ and ‘long-tail’ keywords when ranking websites. Short-tail keywords are single words (such as “shoes”) or short combo nouns (“high heel shoes,” for example). By contrast, a long-tail keyword would be something like “Comfortable high heel shoes for dancing.”
Short-tail keywords help more to set the general context of a page, while long-tail keywords provide more specific details and can help capture highly targeted search queries. A well-balanced approach that incorporates both types of keywords can improve a webpage’s visibility and relevance in search results.
Try to use keywords with a balance of reasonable search volume and manageable competition — you want to find keywords that people are searching for, but that aren’t overly competitive.
Now, let’s take a simple example to show you how you can perform your keyword research. Say you’re selling water heater repair services. Use this as the starting point of your research. So, add the “water heater repair” to various keyword research tools to get more suggestions on what word and phrase variations people are using to search for these services.
There’s all sorts of tools out there — many of them free. For example, WordStream’s keyword tool, which can also show how often a keyword has been searched for.
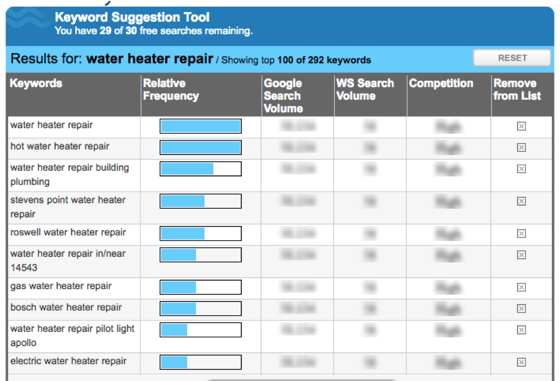
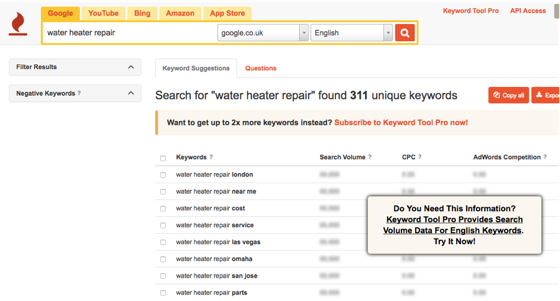
If you click the Questions tab you’ll also see the common questions that users have about “water heater repair” when they search on Google, which is pretty useful as well.
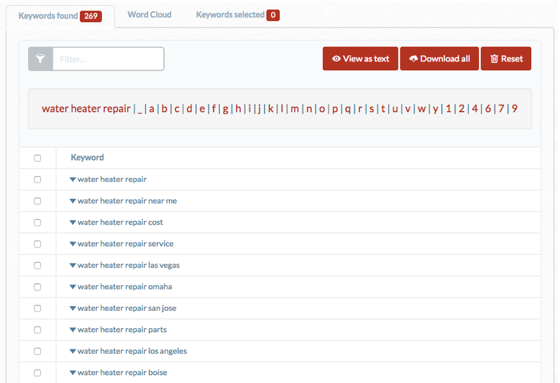
Lots of suggestions here, and they’re organised alphabetically.
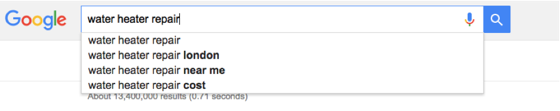
But the fastest option is Google suggest. That’s because it gives you suggestions based on your search even before you hit enter. These suggestions are based on the most common searches that people perform when looking for the product or service you’re selling.
Here’s what shows up when you write “water heater repair” in Google search:
So gather all the relevant keywords you’ve discovered using the above tools and then group them based on things like:
- Product type: e.g. electric water heater repair, ge hybrid water heater repair, Ariston water heater repair
- Location: e.g. water heater repair london, water heater repair near [location of your business]
- Price: e.g. water heater repair cost, water heater repair estimate
Each group of keywords is useful as it helps answer specific questions that prospects might have about your product or service.
So, when writing your page’s content, make sure it includes information about:
- Product: Which types of water heaters can you repair?
- Price: Is there a special offer or discount during the week?
- Location: Do you also cover my area?
- Properties: Is your team experienced in repairing different types of water heaters?
- Extras: How fast can a team come in and repair it?
If your list includes too many keywords and you don’t know which ones can send you more traffic, take a look at the estimated monthly search volume to see how much interest there is and how often people are searching for a specific keyword. For this purpose, you can use your chosen SEO tool to get keyword suggestions as well as estimated search volumes for your keywords.
You can also do SEO competitor analysis to see what your competitors are doing in terms of optimising their sites.
Step 3: Craft your content
Now that you have a better idea of what users are searching for to find a page like yours, you need to start writing your content and optimise it. Fresh, top-quality content is the cornerstone of your interactions with customers and how sites achieve top rankings. By content we’re referring to anything you publish on your site that educates, attracts and delights customers, such as:
- Web page content
- Blog posts
- Ebooks, white papers, and reports
- Brochures, tips sheets, and frequently asked questions (FAQs)
- Sales pages
- Videos
- Pictures, infographics and more
Search engines will crawl your website and try to figure out what it’s about and then decide what queries each of your web pages should rank for. But be sure you write for your visitors first — then for search engines. Don’t sacrifice the usefulness and persuasiveness of your content for SEO-friendly content.
Pay extra attention to:
Titles. Write catchy titles that grab your visitors’ attention.
Keywords. Focus more on adding relevant and useful information that will bring people to your site. Also, combine relevant keywords together and focus on adding varied forms of keywords rather than adding as many keywords as you can.
Topics. Every page needs to focus on a unique topic. At the same time, make sure you don’t optimise more than one page for the same product or intent as this not only causes confusion but you’ll have two pages competing for the same keywords. You don’t want to be your own competitor, do you?
Quality Your content needs to be unique and purposeful. The reason people come to your site is because they’re searching for information, for a solution to a problem so make sure you can provide it to them so they don’t go elsewhere. Find out what Google sees as high quality content.
Freshness. Add new content on a regular basis. You can create a blog where you constantly share information your visitors might find useful, or you can share ebooks or whitepapers.
Length. We recommend having more than 500 words on a page. But the idea is this: your content should be long enough to answer visitors’ questions about your product or service.
An SEO tool can save you lots of time on research. It will show you the type of keywords that users search for on search engines so you know what to focus your page on.
Step 4: Optimise your code
While writing content for people is very important, you need to pay attention to how you optimise your website’s code so search engines can read your content, too. Let’s look at how you can properly optimise your site’s code and help your site rank higher in search engines:
SEO-friendly URL structure
URLs are another important element but often overlooked. If your URLs have gibbering numbers and punctuation marks then, just like users, search engines will have a hard time understanding what that page is about.
Here are a few things to keep in mind if you want to achieve an SEO-friendly site URL structure:
Consolidate your www and the non-www domain versions. If you type in www.example.co.uk into your browser and then you type in just example.co.uk and the “non-www” version does not redirect to www.example.co.uk, that means that search engines are seeing two different sites which is considered duplicate content. This isn’t effective for your overall SEO efforts as it will dilute your inbound links, as external sites will be linking to www.example.co.uk and example.co.uk. So what you need to do is to set your preferred domain, whether with or without www, and implement 301 redirects for all other versions of your URL which will redirect visitors to your preferred domain. It doesn’t matter which URL version you choose as long as you are consistent with it. Here’s how to do a 301 redirect on any platform.
Avoid dynamic URLs. Dynamic URLs are ugly and don’t say anything about what’s on your page. So instead of a www.example.co.uk/?p=3355474 you might want to use static URLs like www.example.co.uk/topic-name. Descriptive URLs allows visitors to figure out what the page is about just by looking at the link.
Use canonical tags. These tags tell search engine bots which pieces of content are the original and which are duplicates. This way the bot will pass over the duplicates and only index and give link credit to the primary piece. To specify the canonical URL, you need to add the rel=”canonical” tag into your URL. Find out how to add canonical tags.
Create an XML sitemap. Sitemaps are like a roadmap for search engines. They include every page on your site, making sure search engine bots don’t miss anything. You can use tools like the XML Sitemap Creator to automatically create a sitemap for you. Once your XML sitemap is created, you should submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools so that search engines can crawl and index your website more easily.
Each page will need a title tag that describes the title of the webpage, appearing in both the browser tab and SERP, providing a brief preview of the content. It needs to be unique and crealy describes what the page is about. Pay attention to the title tag, because it’s one of the key things people see when searching for your products or service. The title tag will also shows up in posts on social media sites. Include your main keyword(s) in the title and entice people to click on it.
Have a unique title tag for each page and include the name of your product or the main topic you’re covering within it. A good title tag ought to be around 40 and 60 characters, including spaces, to make sure the title isn’t cut off. This is a rough guide — and it’s not so much about the number of characters, but the number of pixels they occupy.
The meta description tag
The meta description needs to summarise the content on your page because this too will show up in search engine results together with the title tag. While it won’t help you rank higher, a well-written meta description can have a big impact on whether users decide to click through or not so it should be written to “sell”.
When writing your meta description, make sure:
- You create a different one for each page
- It talks about the features or ideas users would benefit from
- It’s between 100 and 150 characters, including spaces
- It includes a call-to-action that entices people to click.
To exemplify, let’s use the .uk domain page from the 123 Reg website.
Here is how the title tag looks like in the source code:
<title>.UK domain registration | Order your own .uk from 123 Reg</title>
And this is the source code for the meta description:
<meta name=”description” content=”Shorten your existing web address with a .uk domain extension so it’s simpler for your visitors to find your website and remember your brand.”/>
Now, if we run a search for “register .uk domain” on Google, this is what we find:

And if we share this page on Facebook, this is how it looks:

Headings
Heading tags are used to visually break up the content into sections (from a usability point of view) and to tell search engine spiders what that page is about.
In HTML coding the header tags from h1 to h6 form a hierarchy.
The coding should be something like this:
<h1>Main Heading</h1>
<h2>Secondary Heading 1</h2>
<h3>Sub-section of the secondary heading 1</h3>
<h2>Secondary Heading 2</h2>
<h3>Sub-section of the secondary heading 2</h3>
For example, looking at the source code for our .uk domain page, this is how the headings are organised:
<h1>Register a .uk domain from 123 Reg</h1>
<h2>The shorter, sharper extension for UK based sites</h2>
<h2>Why is .uk domain name ideal for you and your business?</h2>
<h2>Who can register .uk domains?</h2>
<h2>Why register a .uk?</h2>
<h2>Search for a .uk domain now!</h2>
When it comes to headings, make sure you:
- Always have a h1 tag on each page but never more than one h1 tag
- Make sure each heading is relevant for the section it represents
Alt tags
Search engine bots can’t see images so you need to help them by adding an alt tag for each image. This alt tag acts as a short description of an image and it can also be a great place to use your keywords and help increase your chances of showing up in image search results.
However, make sure the alt text is relevant to the image. For example, you shouldn’t label an image of a dog with the alt text “affordable online marketing services in London” as it doesn’t make any sense. Don’t try to trick search engines this way, as it could hurt your SEO.
The same goes for your logo image. You need to use logo markup to protect your brand’s logo and prevent it from being hijacked in the way the Gregg’s logo was.
With so many elements that need to be optimised on every single page of your website, you’ll find it saves time if you use an SEO tool. The tool will alert you to any issues the site has, such as missing or duplicate titles and descriptions, more than one h1 tag, missing ALT tags and so on, so you won’t have to check these elements manually across every page on your site.
Interlinking
Interlinking refers to linking on certain phrases or words within the body text of your pages, to other pages, where relevant. If you take a look at this blog post or any other post entry on the 123 Reg blog, you’ll see that we often link to another one of our posts or to a specific page on the 123 Reg website. Basically, we’re linking to other resources that are relevant to a specific topic and that we believe you might find useful.
Why is internal linking important?
- It helps guide users around your website, to other content they might be interested in.
- It helps search engines better understand the relevance of the content on that page.
- It can lower bounce rate. If a user lands on a page on your site and quickly finds a link to something they’re interested in, the chances are they will click on it rather than exit the site.
Here are a few interlinking mistakes you should avoid making:
- Always linking on the same keyword or keyword phrase in hopes that it will increase rankings for that keyword. This is over-optimisation and can harm your SEO. So for anchor texts to work in your favour, they need to be relevant to the content you’ve placed them in.
- Over linking. Don’t link every third word on every page to another page. Only add a link if it’s useful and relevant.
- Broken links. Make sure you always check the pages you’re linking to so that they’re functional.
Step 5: Technical setup
Set up and verify Google Analytics
You need to measure the effectiveness of your SEO efforts and see how your website is performing. How many visitors a month is your site attracting? Which pages are the most popular? How much time are they spending on your site? These are just a few of the things you can uncover by using an analytics tool so make sure you set up your analytics software now so you can start collecting data right away.
Google Analytics is a very good choice because it’s free, easy to set up and use, and provides loads of useful information about your visitors’ behaviour on your site.
Set up Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools
The webmaster tools products from Google and Bing allow you to go more in depth and see things like: who is linking to your site, what search terms are sending visitors to your site, whether your site has any issues that need to be fixed quickly, and more.
Check out the beginner’s guide to Google Search Console to find out how to set it up and what valuable information you can find and use to improve your site.
Install an SEO plugin
If you have a WordPress website, make sure you install an SEO plugin to help you optimise your content. One of our favourites is Yoast. Why? Because it’s free, easy to use and packed with powerful features. Having an SEO plugin like this installed will help you meet all of the recommended SEO criteria with ease.
Robots.txt
The robotx.txt file contains instructions for search engines as to which pages of your site to ignore during the crawl. Basically, this file includes a list of commands, such as allow and disallow, that tells web crawlers which web pages they can or cannot retrieve. So, if a URL is disallowed in your robots.txt files, that URL and its contents won’t appear in Google search results.
Make sure you’re not stopping search engines from indexing your site. While some prefer to use the “disallow: /” command while their site is under construction, it’s important to remember to remove it once the site is ready to receive visitors.
Step 6: Earn links
Links are an important ranking factor and continue to be a great indicator of what content is relevant and important.
However, it’s not about getting hundreds of links quickly but about getting quality and authority sites to link to your website.
Today your link building strategy should be about earning links, which you can do by:
- Creating purposeful content (for example, guest posts or infographics) that is so useful and engaging that people want to link to it and share it with others.
- Promoting your content so that it reaches the right people who will be motivated to link to your content and share it online.
- Building relationships with influencers and convincing them that your content is of a high enough quality to share.
Read our post for more great ways to earn backlinks for your small business site.
Step 7: Things to check post-launch
Test usability
Usability is super-important for SEO and it also helps keep your visitors happy. Great user experience refers to a site that is easy to navigate through, with information that’s easy to find and useful.
Test your site’s usability yourself (or ask your friends), as if you were a customer. Check to make sure there aren’t more steps than necessary in the checkout process and that it’s easy for visitors to navigate through your site, to buy a product and to contact you.
Test your site speed
Site speed is an increasingly important ranking factor, so don’t forget to test your site’s speed and improve loading times if necessary. You can check the loading time for each of your web pages by using Google’s PageSpeed insights tool. If the speed is less than 90, you will need to make some changes such as optimising and compressing images, and loading scripts after your website’s main content, wherever possible.
At this time having a web developer is useful as you can send them a link to the site speed report and ask them to follow instructions supplied by Google in order to increase your pages’ loading time.
Check your mobile website
Having a website that works properly on all devices – desktops, tablets and smartphones – is extremely important. With mobile devices now driving 56% of traffic to top sites and with mobile-friendliness now a ranking factor, you need to make sure that your site is mobile-ready and that there aren’t any issues. You can learn more about the importance of mobile-friendly design here.
Conclusion
Following these simple SEO steps will set a healthy base for your website so it can receive more organic traffic. Just remember to be patient, as it takes time for search engines to index your site and start ranking it. When it comes to SEO there aren’t any shortcuts. If you do anything shady to speed things up, you might be caught and actually appear further down the rankings — and that’s it’s not worth it. The main thing you should focus on is creating a site with top-quality content that gives users what they’re looking for, optimising it for search engines so that people can find it easier online.
The bottom line: It takes time and it’s a lot of hard work but if you stick with it and do it right, it does pay off.

Download your SEO checklist here — and have it with you to optimise your website.
What would you say is the most difficult task when optimising a new website? We’d love to hear from you so tweet us at @123reg.



